Understanding Bursitis
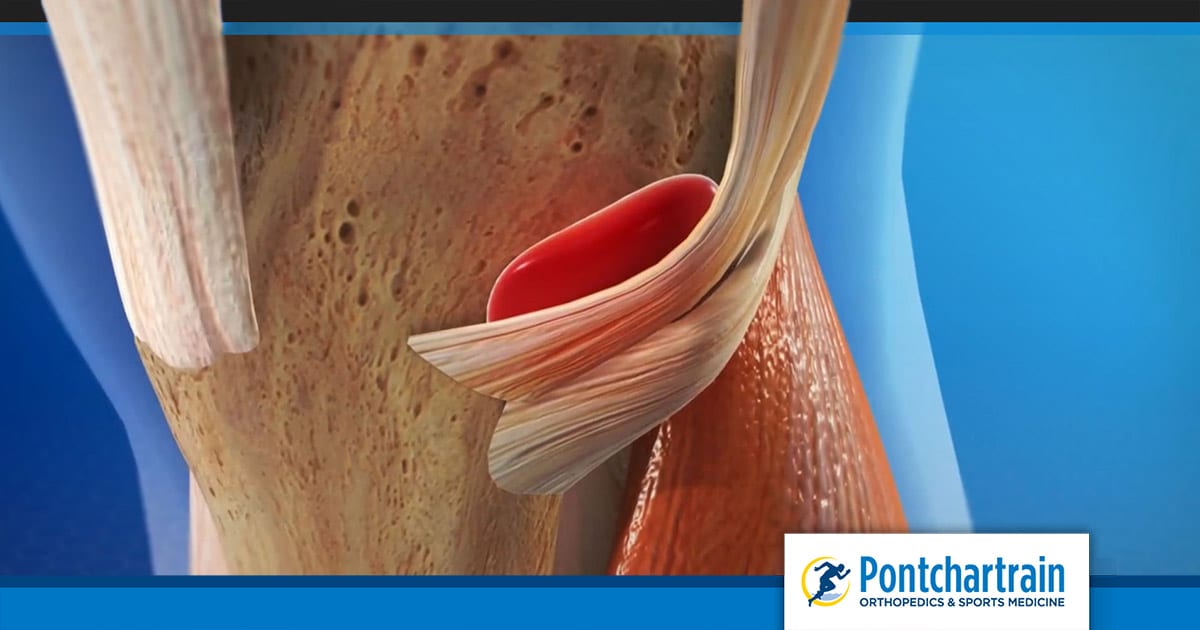
Joint pain can range from mildly annoying to very debilitating. When it’s severe, it’s easy to jump to the worst conclusions. Sometimes, the diagnosis of joint pain is a common, treatable condition which can affect just about anyone--bursitis. Understanding bursitis starts with a description of its symptoms, what it’s sometimes mistaken for, and how to quickly treat it.
What is bursitis?
Understanding bursitis starts with the bursae. Bursae are small pads filled with fluid--there are over 150 bursae in your body. A bursa is like a cushion in your joint between your bones and tendons. When the bursa is healthy and not inflamed, your joints move smoothly and pain-free. However, if your bursa becomes swollen, inflamed or injured, you will have pain and swelling in your joints. Bursitis can affect any joint, but the most frequently affected areas are the shoulder, elbow, hip, and knee.
What causes bursitis?
Anyone can get bursitis; however, it’s more common in people who do repetitive movements, especially movements requiring weight or pressure on joints.
There are several causes of bursitis, but here are some of the main ones:
“When treated quickly and effectively, bursitis can improve in weeks.”
- Joseph L. Finstein, MD
Symptoms of Bursitis
The primary symptom of bursitis is pain. Other, typical symptoms of bursitis are:
What can bursitis be mistaken for?
On one end of the spectrum, bursitis is sometimes written off as an ache or pain. It might be seen as mere stiffness or maybe arthritis. Conversely, severe joint pain might be mistaken for joint failure or, in extreme cases, cancer. Understanding bursitis begins with a correct diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Bursitis
Quickly and effectively treated, bursitis will improve in weeks. Bursitis rarely requires surgery and is treatable by a variety of options.
Common Bursitis Treatments May Include:
Modified activity
Avoid tasks and activities that make bursitis pain worse.
Anti-inflammatory medication
NSAIDs - nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen reduces pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy
Strengthening the joint and surrounding muscles can reduce pain and swelling.
Steroid injections
Ultrasound guided injections effectively pinpoint and treat pain. In this procedure, the physician will inject anesthetic and steroid into the bursa to alleviate pain. More about ultrasound guided injections...
Regenerative therapies
Using new technology, the physician uses an amniotic membrane allograft and injects signal cells into the injury site. The patient’s cells then regenerate the damaged tissue. More about regenerative therapies...
If non-surgical treatments don’t help with bursitis pain, arthroscopic surgery has proven effective as a minimally invasive way to treat this condition. During arthroscopic surgery, the inflamed bursa and any surrounding impediments like bone spurs are removed to enable the tendons to move more freely.
Why you should see an orthopedist
Don’t wait to treat your joint pain. Understanding bursitis and your treatment options is critical. Remember, bursitis can appear to be many different conditions than what it is--only a professional can tell you the cause of your joint pain. Correctly diagnosed and treated, bursitis is a very manageable condition. There is no need to suffer with joint pain caused by bursitis--contact us today for an accurate diagnosis and find out what treatment options are available to you.
About the Doctor

Dr. Joseph L. Finstein, MD
Joseph L. Finstein MD specializes in sports medicine including injuries of the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, foot, and ankle.
Dr. Finstein completed his Orthopedic Surgery residency at Hahnemann University Hospital/ Drexel University where he served as the Administrative Chief resident and won multiple awards including Most Outstanding Resident and Most Outstanding Resident Teacher. He concluded his medical training with a Sports Medicine Fellowship at the Rothman Institute at Thomas Jefferson University.
This website is not designed to and does not provide medical advice, medical diagnosis, professional opinion, treatment or services to you or any other person. Through this website and links to other websites, Pontchartrain Orthopedics & Sports Medicine provides general information for educational purposes only. The information provided in this website, or through links to other sites, is not a substitute for medical care. You should not use this information in place of a visit, call, consultation or the advice of your healthcare provider. Pontchartrain Orthopedics & Sports Medicine is not liable or responsible for any advice, course of treatment, diagnosis or any other information, services or product you obtain through this site.
