Bone Fractures
Bone fractures, also known as bone breaks, are a break or crack in the bone caused by falls, high impact accidents, and sports injuries. When force is applied to a bone that it cannot withstand, it may break. Sometimes the amount of force isn’t that intense; however, the angle of the force or the condition of the person can also determine when a break occurs. Those with additional conditions like osteoporosis, diabetes, or arthritis may be more susceptible to bone breakage. Small children and those advanced in age may also be more likely to sustain broken bones.
Common bone fractures include the collarbone, forearm, wrist, hip, and ankle. Hands and fingers, as well as feet and toes may sustain broken bones as well, but these injuries are complicated to repair because of the nature of the limbs.
Types of Bone Fractures
Bone fractures range in severity and appearance. Bone fractures are sometimes referred to as a complete fracture. In this type of fracture, the bone will snap into two parts—sometimes more. If the bone breaks through the skin, it is called an open fracture. There are several specific types of bone fractures including:
Avulsion fracture
Avulsion fractures are when a tendon or ligament and bone are pulled in the opposite direction. A piece of the bone can come off with the ligament or tendon. Although the bone is still somewhat intact, a break has occurred.
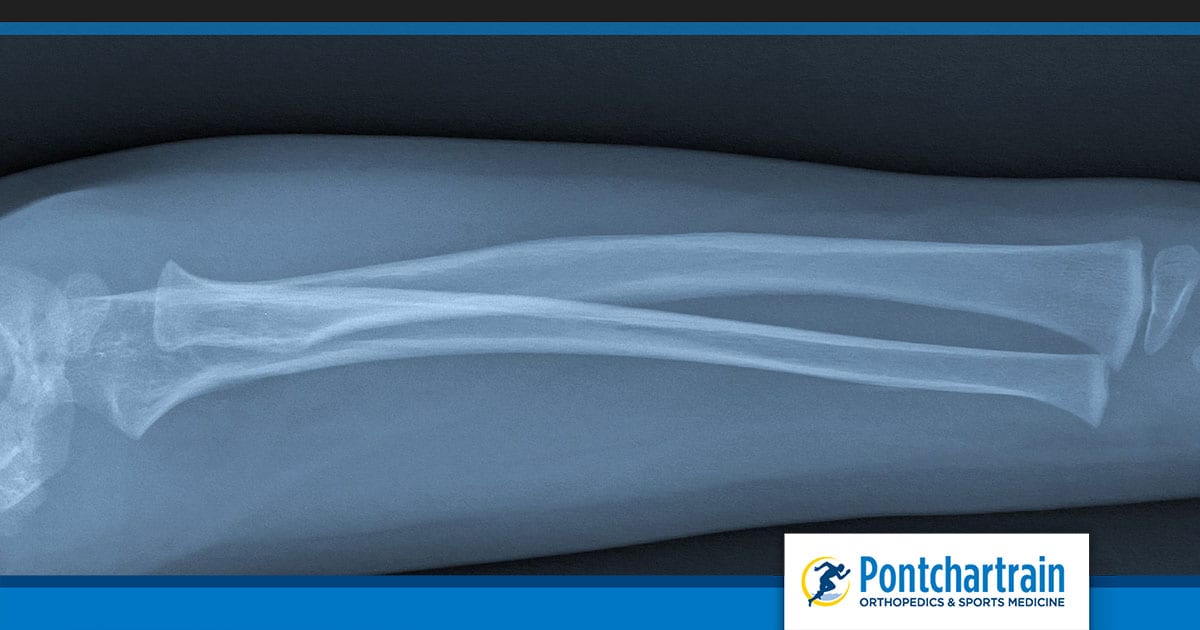
Transverse fracture
A transverse fracture occurs when the bone breaks at a 90 degree angle. It is usually a result of a blow to the bone. This is the most severe fracture.
Oblique fracture
An oblique fracture is a break that occurs at an angle to the bone as a result of a twisting injury. These breaks often occur in the leg bones like the femur, fibula, or tibia.
Comminuted fracture
With a comminuted fracture, the bone generally breaks into several fragments and can occur in any bone.
Greenstick fracture
A greenstick fracture occurs in children with undeveloped bones. These breaks are when the bone bends but doesn’t break completely.
Stress fracture
Stress fractures are caused by repeated stress and can be a hairline fracture. They don’t appear broken externally, but are still quite painful.
Pathologic fracture
Bone fractures are also caused by diseases (like osteoporosis and cancer) where the bones become weaker and more brittle.
Symptoms of Fractures
Symptoms of bone fractures include swelling or bruising near the site of the injury, pain ranging from tenderness to severe pain in the injured area, loss of function, or deformity of the affected limb.
Nonsurgical treatment of a broken bone
Slings and splints
Slings are used for arm or shoulder breaks. They foster healing by holding the limb still. Splints are more rigid and are used after surgery to hold the limb steady until swelling subsides.
Casts
Casts are made from plaster or fiberglass and hold the bone still so that it can heal. Casts limit muscle movement, which offers additional immobilization.
Bone stimulation
Bone stimulation is either electronic or ultrasonic and facilitates the healing process. With the use of electrodes on the skin, low electrical currents are sent into the bone. This speeds up healing.
Surgical repair of a broken bone
Open reduction and internal fixation
When bones need additional support than a cast can provide, surgical repair is suggested. In open reduction and internal fixation, metal rods, screw, or plates are used to reposition and stabilize the bone.
Closed reduction and external fixation
If a complex fracture is unable to be repaired with open reduction, it must be secured with an external frame. This frame holds the bone in the correct position so that it can heal. The frame may be temporary or long term.
Healing process for broken bones
If bones are not treated in a timely manner, they may not heal properly. There are other causes of bones not healing, which include infections after fracture, not enough blood flow to the bone, or insufficient stabilization of the broken bone. When any of these conditions occur, bones can experience malunion (fracture heals in an incorrect position), delayed union (fracture heals slowly), or nonunion (fracture fails to heal). With treatment from an orthopedic specialist, broken bones typically heal in 6-12 weeks.
